We will now set up the system for a QM/MM simulation with Gromacs. The
dimerized thymine bases will be described at the semi-empirical AM1
level of theory, while the remainder of the system is modeled with the
Amber99 forcefield. Figure 3 shows how we split up our system in a QM
and MM part.
The QM/MM division splits the systems along a chemical
bond. Therefore, we need to cap the QM subsystem with a so-called link
atom (la, figure 4). This link atom is present as a hydrogen atom in
the QM calculation step. It is not physically present in the MM
subsystem, but the forces on it, that are computed in the QM step, are
distributed over the two atoms of the bond. The bondlength itself is
constrained during the computations.
To make use of the QM/MM functionality in Gromacs, we have to
Adding Link Atoms
At the bond that connects the QM and MM subsystems we introduce a link
atom. In Gromacs we make use of a special atomtype, called LA. This
atomtype is treated as a hydrogen atom in the QM calculation, and as a
dummy atom in the forcefield calculation. The link atoms, if any, are
part of the system, but have no interaction with any other atom,
except that the QM force working on it is distributed over the two
atoms of the bond. In the topology the link atom (LA), therefore, is
defined as a dummy atom:
All required amber forcefield fiels are available for download here:
amber.tar,
uncompress the file with
tar -xvf amber.tar
Specifying the QM Atoms
Once we have decided which atoms should be treated by a QM method, we
add these atoms, including the link atoms, if any, to the index
file. We can either use the make_ndx program, or hack the atoms into
the index.ndx file ourselves. The index file we will use in this
tutorial is found here: qmmm.ndx. It
is possible to constrain the bonds in the QM subsystem along. It is
also possible not to constrain them, while the bonds in the MM
subsystem are. This is essential for instance if the QM atoms are
supposed to undergo bond-breaking/formation reactions. In this case,
Gromacs' bondtype 5 is used for the bonds in the QM subsystem:
Specifying the QM/MM Simulation Parameters
The last thing we need to do to setup gromacs for performing QM/MM
calculations is to specify what level of QM theory gromacs has to use
for the QM subsystem, what QM/MM interface to use, what multiplicity
the QM subsystem has, and so on. All these things are defined in the
mdp file. The following option lines need to be included for a QM/MM
run:
With this setup, we will perform a short 1ps QM/MM MD simulation.
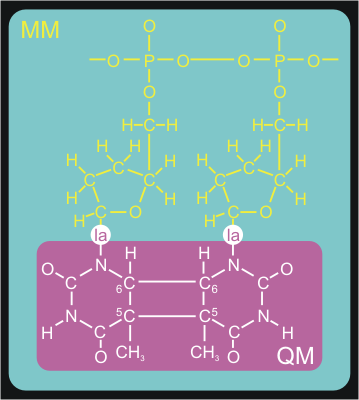
Figure 3. Division of the system in a QM
subsystem and an MM subsystem. The QM subsystem is described at the
semi-empirical QM level, while the remainder of the system,
consisting of the reactants-aliphatic tail is modeled with the Amber99
forcefield. Link atoms are introduced at the QM/MM boundary to cap the
QM subsystem.
[ dummies2 ]
Note, a link atom has no mass.
LA QMatom MMatom 1 0.73
Furthermore, the bond between the MM and QM atoms is maintained at the
forcefield level:
[ bonds ]
Note that, because in our system the QM/MM bond is a carbon-nitrogen
bond (0.153 nm), we use a constraint length of 0.153 nm, and dummy
position of 0.65. The latter is the ratio between the ideal C-H
bondlength and the ideal C-C bond length. With this ratio, the link
atom is always 0.1 nm away from the QMatom, consistent with the
carbon-hydrogen bondlength. If the QM and MM subsystems are connected
by a different kind of bond, a different constraint and a different
dummy position, appropriate for that bond type, are required. Note
that because the link atoms are constructed at each step of the
simulation, it is not relevant a what position the link atoms are
introduced in the configuration file. Thus, we can simply place the
two linkatoms at the origin (0,0,0). Click to have a look at what the
structure and
topology files should look like for a
QM/MM simulation.
QMatom MMatom 1
[ bonds ]
QMatom1 QMatom2 5
QMatom2 QMatom3 5
QMMM = yes
Note that the default options are shown here. The actual options
depend on the system. The mdp file we will use for the short QM/MM
equilibrtion simulation is located here:
qmmm1.mdp. In case one choses as the
QMmethod a semi-empirical method, such as AM1 or PM3, the
QMbasis is ignored.
QMMM-grps = QMatoms
QMmethod = RHF
QMbasis = STO-3G
QMMMscheme = ONIOM
QMcharge = 0
QMmult = 1