We apply the flooding potential in all collective degrees of freedom and continue the QM/MM simulation. We use the last frame of the previous QM/MM simulation as a starting structure for the flooding run:
grompp -f qmmm2.mdp -p qmmm.top -n qmmm.ndx -c qmmm2out.gro
./mdrun -v -c qmmm3out.gro -ei sam.edi -x traj_VII.xtc
Again, since the run will take up to 40 minutes, we have made the output available for you to download: electron2.tar.
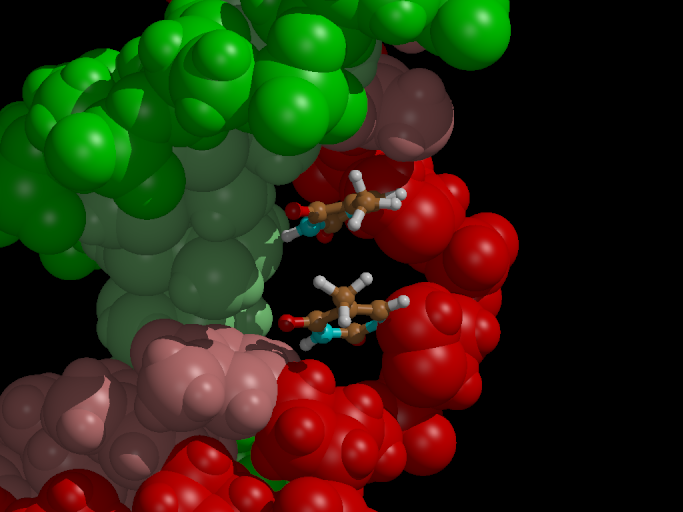
The last frame of the flooding simulation is shown in Figure 5. We see
that both covalent bonds between the bases are broken. However, there
is still an excess electron on one of the bases, which is reflected by
the sp3 hybridization of the pyrimidine nitrogen atom.
In reality, the electron is transferred back, either to the FADH
cofactor in Photolyase, or to an adjacent base in the DNA strand. To
account for this back-transfer in our simulation, we continue the
simulation from the last frame, using the old
mdp file for the neutral singlet QM
subsystem.
grompp -f
qmmm1.mdp -p qmmm.top -n qmmm.ndx -c
qmmm3out.gro
./mdrun -v -c
qmmm4out.gro
The output files are available here: final.tar.
The last frame of the simulation is shown in Figure 6. We see that the
DNA is completely restored!
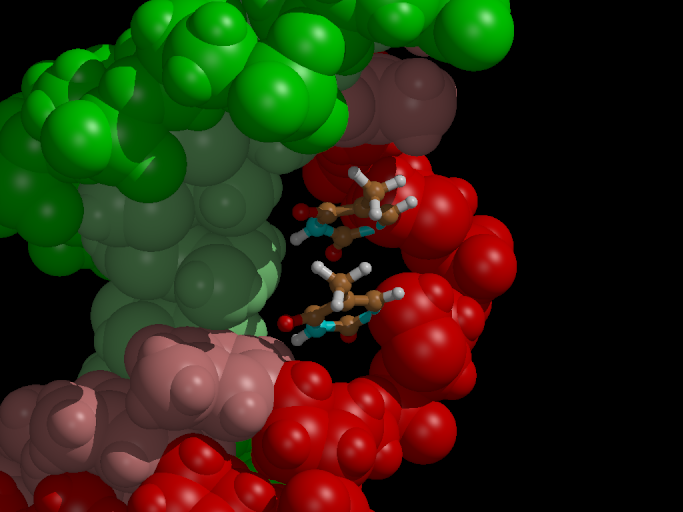
Figure 5. With the flooding potential the
thymine dimer is completely broken within 2 ps.